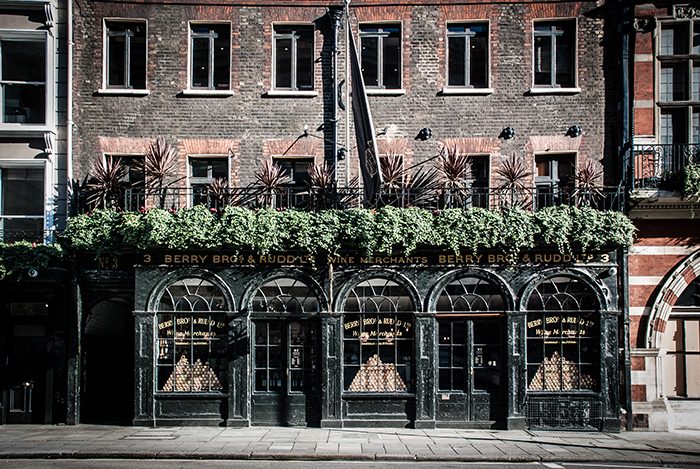
Recent news that Berry Bros & Rudd is announcing a consultation over job cuts came as a surprise to me, given that luxury markets are typically the most protected from wider market difficulties. The new duty rates only represent a small increase for high-value wines and premium customers tend to be far less sensitive to belt-tightening than mass-market consumers.
The company itself has cited global market conditions, high inflation and rising national insurance contributions as factors behind its decision. Although one might assume Berry Bros & Rudd and/or customers could absorb these challenges, ‘global market conditions’ can mask multiple underlying issues.
Part of their business depends on a buoyant wine investment market, yet Liv-ex data shows the bid-to-offer ratio reaching historical lows, suggesting a downturn in investor enthusiasm.
Another part of their operation relies on continued faith in the antiquated and now fragile En Primeur system. The 2023 Burgundy En Primeur vintage pricing has left buyers wary, particularly when older vintages can be cheaper than new releases. A major producer, Bouchard Père & Fils, has already pulled out of the En Primeur process, unsettling the market further.
While the new duty rates are not especially burdensome for expensive wines, paying more for wines still in bond creates discomfort for some buyers and the long-term costs of holding and ageing wine may have been overlooked in En Primeur pricing.
Nevertheless, the luxury wines and spirits market overall is showing strength, buoyed by some younger, affluent consumers in the millennial and Gen Z demographics who are gravitating towards exclusive products perceived as status symbols. The generational shift in tastes may place traditional regions, sold by traditional companies, at a disadvantage as younger buyers branch out.
E-commerce platforms and direct-to-consumer models are also reshaping how, even luxury, products are bought and sold, enabling newcomers to engage with a wider audience in a more personalised and efficient manner.
Despite some positives, recent events at Berry Bros & Rudd highlight the complexities within the industry, where global trends, long-standing practices and changing demographics can converge to create unexpected challenges, even at the very top end of the wine market.