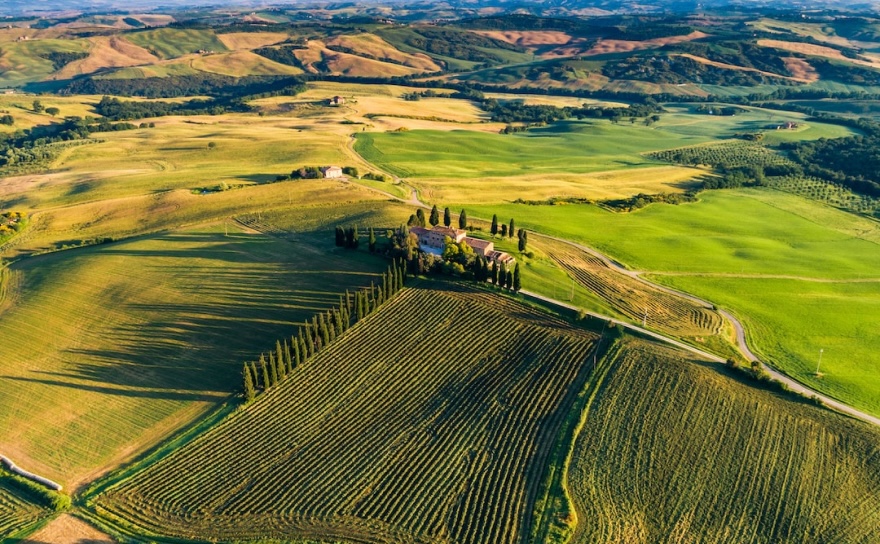
The Rioja region of Spain stretches from Tormantos to Alfaro and represents a tapestry of diverse climates, terrains and winemaking traditions. The 100 km expanse between these western and eastern limits encompasses the Atlantic and Mediterranean climates, fostering a unique environment for viticulture.
The name ‘Rioja’ comes from the River Oja (Rio Oja in Spanish), which flows through the region. The region’s vineyards are beautifully arranged on hillside terraces, reaching altitudes of up to 900m.
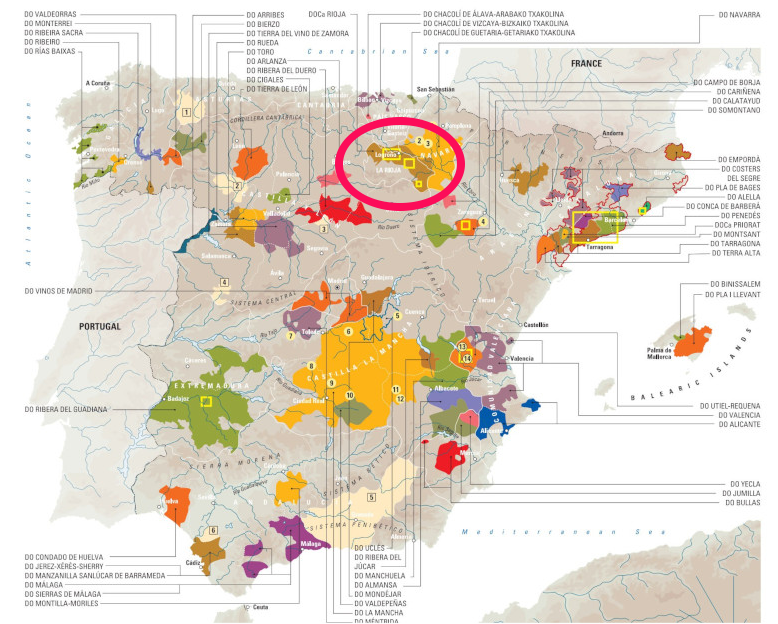
The Rioja wine region is a mosaic of 571 wineries distributed across 144 municipalities in three different Autonomous Communities: La Rioja, the Basque Country, and Navarre, with an additional winery in Castilla y León. Since 1991, these wineries have been united under the Quality Designation of Origin (QDO) Rioja, that represents a commitment to the highest and strictest quality standards. Rioja’s distinction as the first QDO in Spain and one of only two nationally to meet these rigorous standards.
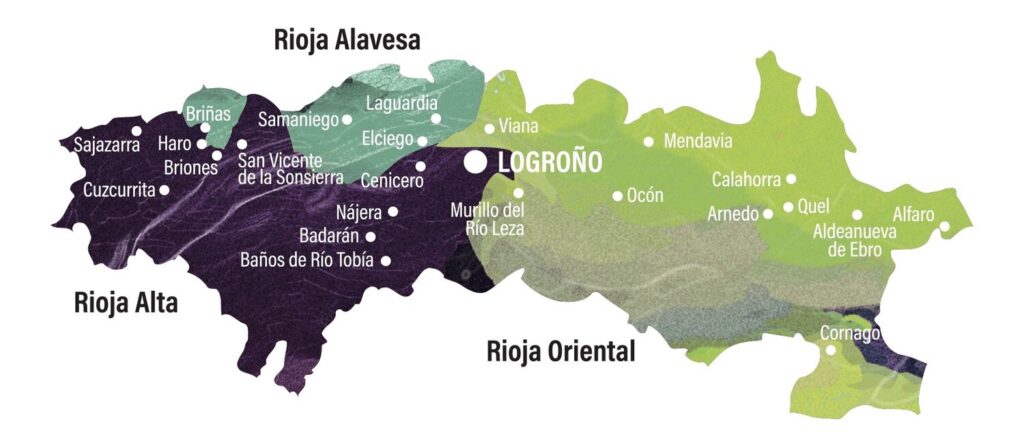
Rioja is traditionally divided into three distinct zones, each contributing its unique character to the wines produced:
- Rioja Alta: Located in the western, higher part of the region, Rioja Alta is renowned for its winemaking town of Haro, home to many prestigious bodegas such as Muga, CVNE, La Rioja Alta, and Roda. The vineyards here, perched high on the slopes of the Sierra Cantabria, enjoy a late ripening of grapes that retain a lively acidity, ideal for producing wines with excellent ageing potential.
- Rioja Alavesa: Situated further east in the Basque country, Rioja Alavesa shares many characteristics with Alta. The vineyards around the towns of Laguardia and Elciego are known for producing some of the region’s best grapes. The red wines from Alavesa are celebrated for their pure fruit flavours and enchanting aromas.
- Rioja Oriental: In the southern, eastern section of Rioja, the warmer, more Mediterranean climate favours the growth of Garnacha, producing distinctive wines that reflect the region’s diverse terroir.

At the heart of Rioja’s winemaking is the Tempranillo grape. This versatile grape produces abundantly fruity, light wines that develop grace, silkiness, and a perfumed character through oak ageing. A typical Crianza from Rioja is primarily a blend of Tempranillo with Garnacha, adding body to the wine. Graciano, a Rioja speciality prized for its aroma and acidity and Mazuelo, known locally as Carignan, which contributes tannin and colour, are also integral to the blends.
Rioja Blanco, the region’s white wine, has undergone the most significant transformation. Traditionally made from Viura, Malvasia, and Garnacha Blanca, these wines were once known for their oak-aged complexity. However, contemporary styles favour a more neutral, fruity profile.
The ageing process of Rioja wines is categorised into four main stages:
- Joven: Wines that have undergone no oak ageing.
- Crianza: Wines aged for a minimum of one year in oak barrel and one year in bottle before release.
- Reserva: These wines spend one year in oak barrel and two years in bottle, often representing some of Rioja’s finest.
- Gran Reserva: Typically produced in the best vintages, these wines are aged for two years in oak barrel and three years in bottle.

Rioja’s wine region is a vibrant and diverse landscape, offering a rich array of styles and flavours.