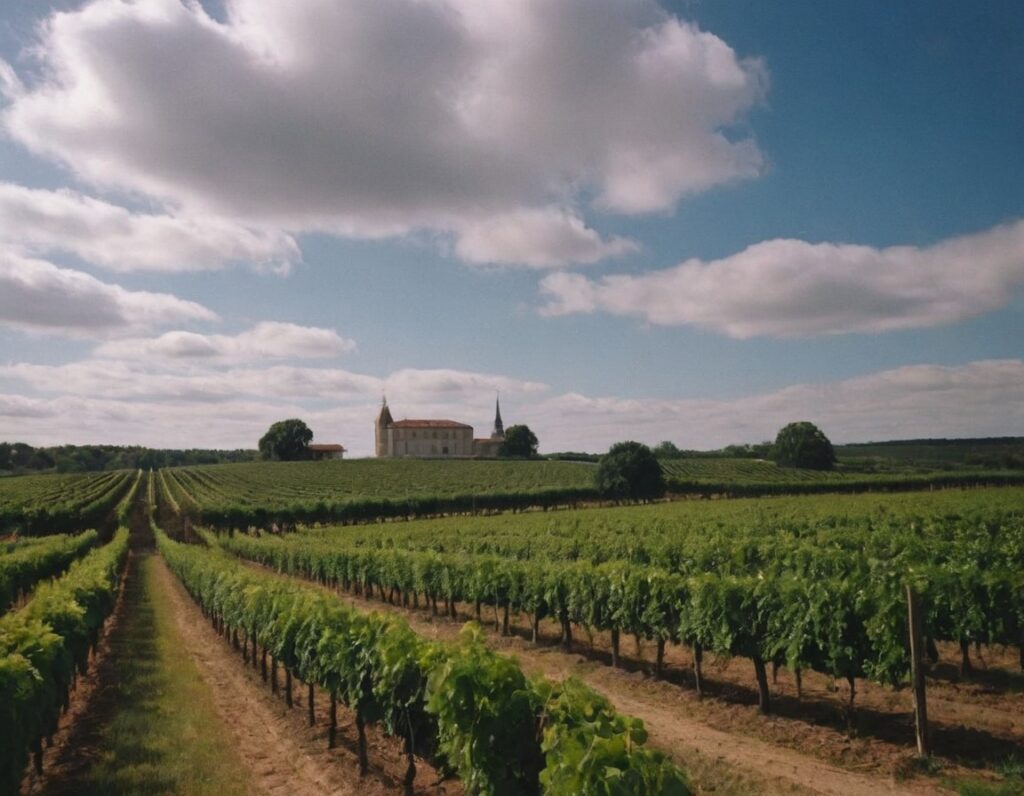
New research examines the impact of climate change on the income of wine producers in the Bordeaux region. The study analyses the relationship between climate variables, vineyard characteristics and economic performance. The findings indicate that rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns significantly affect vineyard yields and income, with high temperatures during the bloom period (May to July) reducing yields, while warmer conditions during ripening (August to September) have a positive effect. Rainfall variability, particularly excessive precipitation during the bloom period, also negatively impacts yields.
Wine producers in Bordeaux have responded by adapting their business strategies. Many have expanded their vineyard area to compensate for lower yields and have prioritised operational expenses over long-term investment. Risk management strategies such as irrigation and crop insurance have been widely adopted. The study also highlights differences in adaptation based on the value of wine production, with high-value producers implementing more sophisticated strategies.
Over the past decades, a gradual increase in temperature, a slight decrease in rainfall, and fewer frost days have been observed. These changes have contributed to a shift in vineyard structure and management. Despite declining yields, wine producers have attempted to maintain income by focusing on quality rather than quantity, as indicated by the rising unit price of wine. Financially, farms have faced increasing operating costs and a decline in net investment, suggesting short-term adaptation strategies.
Looking ahead, the future of Bordeaux’s wine industry will largely depend on how climate trends evolve and how effectively producers adapt. If the current trajectory of rising temperatures continues, by 2050, Bordeaux may experience a significant shift in its viticultural landscape, potentially losing up to 85% of its traditional production areas. With projections indicating further increases in extreme weather events, including heatwaves and irregular rainfall, yields could decline even more sharply, particularly for producers unable to invest in adaptive strategies. However, advancements in drought-resistant grape varieties, improved irrigation techniques and financial tools such as climate-indexed insurance could help mitigate these losses. Without further adaptation, revenue per hectare may continue its downward trend, while production costs will likely rise due to increased spending on protective measures. Conversely, if adaptation is successful, Bordeaux could see a transformation towards a model focused on lower-yield but higher-value wine, preserving economic sustainability despite the challenges posed by climate change.